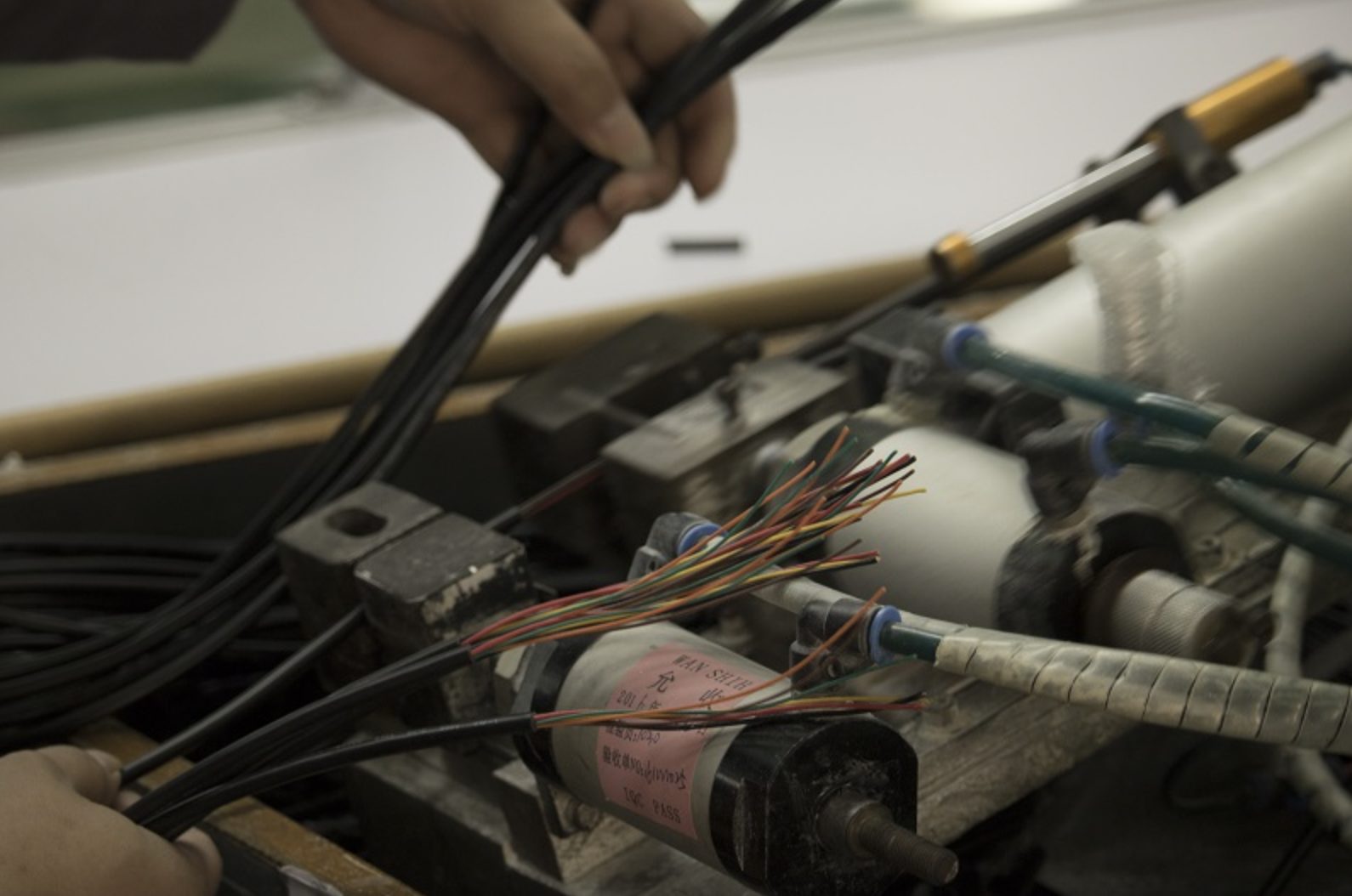
A wire harness is a collection of cables, connectors, and wires to send signals or power over an electrical network. The strip, crimp, solder, and assemble wires in various configurations are all included in complete on-site services.
Wire management items like tie wraps, split loom tubing, and a variety of sleeving are used in Electrical Harness design assemblies to bind wires together in a safe and secure routing pattern with maximising efficiency.
Steps of Electric Wire Harness Design
1. Designate Wire Processing
The types of machines best suited for application will be more precisely determined by the gauge of wire and the variety of end treatments in the project. For wire gauge and end treatment options, the machines only have a finite number of moulds for wire gauge and end treatment options.
Wire marks are another similar measure. The process and machine selections will be based on the different markings kinds. The money and machine space come into play after the specifications are established.
2. Developing allotment and slot requirement
The slot increases as the device’s features and options increase. It is a completely automated wire processing machine that can handle six different wire kinds and twelve different end treatments. It has a correct laser wire marking option that n will be significantly higher than the primary wire-cutting machine.
3. Updating Design Process
The wiring of the logical design must be supported by the design process. To provide the best process flow, the design solution is essential. The solution or design process is challenging to implement and prone to mistakes. Automotive design engineers‘ automation would not do much to prevent those errors from happening sooner. Consequently, this slows down the fabrication of harnesses as a whole.
4. Managing Wire and Component Details
Engineering teams are constantly improving the design time by finding efficiencies. As a result, engineering teams lack the motivation to bear the expense of keeping track of and storing manufacturing needs.
Additionally, manufacturing information for cabinets and harnesses can not always be included in the design projects by electrical designers. The manufacturing tips are frequently fundamental knowledge obtained through trial and mistake on the factory floor.
Common Mistakes and Advice
The technical information about the parts is the essential part of knowledge, like logical connectivity, wires, etc. For instance, if the maximum and minimum wire diameters for any connection are readily available, the design team can avoid making typical mistakes.
The wire diameters should ideally match the component data automatically and the design solution. The operational needs and physical restrictions all help to guarantee the design’s accuracy. Early on, a design solution can be driven more effectively with more information about the machine and wiring.
Conclusion
In the last few years, wire harness processes have been greatly accelerated by technological developments in wire processing. Today’s machines go beyond simple cut, mark, and strip machines.
The processing of many wires, end treatments, wiring sequences, and even wire insertion into connectors are all made possible by impressive automation choices. Therefore, it is more important than ever to have a robust design process to record design intent, assembly guidelines, and production specifics.